Diamonds come in all varieties of shapes, sizes, colours, and with unique internal characteristics. Their value varies significantly based on the four main quality factors - The 4Cs - Cut, Colour, Clarity and Carat. Read more below to help you choose the right diamond for you.
Book an Appointment

The 4C's
There are 5 Cut Grades, however as standard we offer only the top 2, Very Good and Excellent because Cut, along with Colour is integral to a bright and beautiful diamond. Generally, the higher the Cut Grade, the brighter the diamond.
We always recommend Excellent Cut for the best quality diamond.
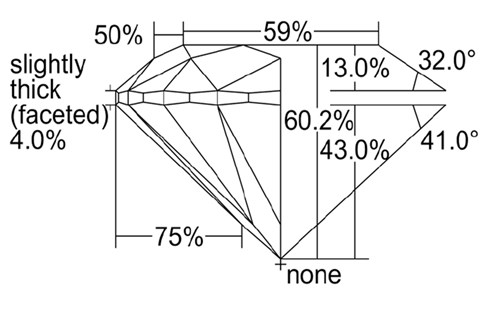
Proportions are crucial to the beauty and value of the diamond as poorly balanced proportions negatively affect the light performance (brilliance, fire). This is often clearly visible to the eye as the diamond looks dull and lifeless, or "lopsided".
A well proportioned diamond looks pleasant to the eye and the stone is cut evenly with a table that is not too wide or narrow, and pavilion that is not too deep or shallow in relation to the rest of the stone. The light enters through the crown of the diamond and returns the same way to the eye of the viewer, creating the unique pattern visible on each diamond.
Pattern refers to the size, contrast and arrangement of light ("brilliance" or "sparkle"), dark ("scintillation") and colourful ("fire") areas on the face of the stone, and is often seen as a recognisable precise arrow pattern on high quality Round Brilliant Cut diamonds.

Colour
Diamond Colour is the second most observable quality factor and subtle differences in colour can dramatically increase or decrease the value of the diamond.
At Daniel Christopher we recommend diamonds from D (colourless) through to H (near colourless) grades; however we understand that individual tastes vary from person to person and are happy to source specific diamonds upon request.
The normal diamond Colour Grades range from D (colourless) though to Z (light yellow or brown), and colourless diamonds are the most rare, and hence most valuable.
Diamonds in the D-F colour range are pure white, with the difference being the transparency of the stones. Diamonds in the G-J colour range are described at near colourless, with G and H colour grades still appearing white, unless compared directly next to a colourless stone. Diamonds with Colour Grades K and below will clearly appear tinted.
Each grade is not a specific colour, but a range of colour. The ranges at the top end of the colour scale are much smaller than the ranges at the lower end of the colour scale.
Diamonds outside of the normal colour range fall into the Fancy Colour Range and can display any colour other than white or brown. The most common (although still extremely rare) are Fancy Yellow diamonds; with Pink, Blue, Purple and Red amongst the rarest of them all.
A diamonds colour is caused by minerals, normally Nitrogen, being present deep in the earth's crust while the diamond is formed.
FLUORESCENCE
Fluorescence refers to the strength or intensity of a visible light (normally blue) that some diamonds emit when exposed to long-wave ultraviolet light.
Fluorescence is present in around 35% of all diamonds and in most them, it has no noticeable effect on appearance. In rare cases, very strong fluorescence can make the diamond look hazy or oily.
Fluorescence is caused by trace amounts of the element Boron present within the diamond. Because no fluorescence means that this element is absent (therefore making the diamond more pure carbon), less fluorescent diamonds tend to be more highly priced. However, in some cases medium to strong fluorescence is preferred, for example in tinted Colour Grades. Fluorescence has no effect on the structural integrity of the diamond.

Clarity
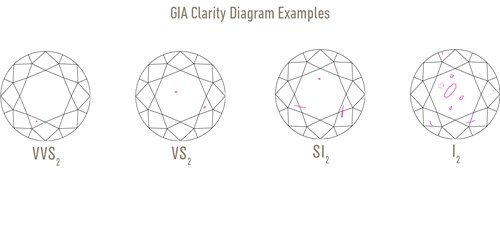
Diamond Clarity refers to how many imperfections (inclusions and blemishes) there are within a diamond. At Daniel Christopher we recommend Clarity Grades of SI1 and above.
Clarity is important to the value of the diamond because visible marks can negatively affect the appearance, symmetry, pattern and brilliance of it. Nearly all diamonds have inclusions (internal imperfections) and blemishes (external surface imperfections) to a varying degree, and those with the least imperfections are rewarded with the highest Clarity Grades. The higher the Clarity Grade the more expensive the diamond tends to be.
Diamonds that have small minute inclusions are often preferred to "flawless" or "perfect" diamonds as they add "character" to the diamond and help identify each unique natural diamond and separate them from imitations.
In fact, "flawless" or "perfect" diamonds do not exist in the natural world and Flawless Clarity Grade (FL) refers to no inclusions or blemishes being visible at 10x magnification.
Imperfections were created when diamond was forming deep in earth's crust and are either distortions in the diamond crystal or particles of other elements.
Even a slight change in carat weight can make a significant difference to cost price, and is therefore measured with high accuracy with specialist machines. Price also tends to increase disproportionately the heavier diamonds get. For example, a price of a 2 carat diamond is likely to be more than double the price of a 1 carat diamond, all other factors remaining the same (Cut, Colour and Clarity).

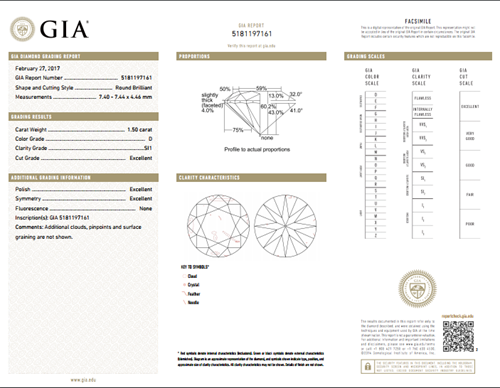
How to read a diamond grading report
Diamond Grading Report or Certificate is issued by gem laboratories for individual stones, usually larger than one carat, but now more and more also for smaller stones under a carat, to certify that the stone is a genuine natural diamond, and to evaluate each of the quality factors described above - Cut, Clarity, Colour and Carat.
Other information included in the certificate are Cut Grade, Polish and Symmetry, Fluorescence and Measurements of the stone, and any additional comments or information (i.e. inscriptions) relevant to this particular diamond.
At Daniel Christopher, we always recommend GIA (Gemological Institute of America) certified diamonds due to their strict and highly developed grading criteria, and the GIA system being universally accepted.
It is becoming more and more important to only purchase GIA certified diamonds to ensure that what you hold is indeed a genuine high quality natural diamond (as opposed to low quality or synthetic lab-grown).
All GIA Diamond Grading Reports are available for you to search at the GIA website using the certificate number.